Inspiration struck Toby Marlow during a comparative poetry class at Cambridge University in fall 2016. Participating in a discussion on William Blake, he found his mind wandering and began scribbling a series of unrelated notes: “Henry VIII’s wives → like a girl group … Need Lucy!!”
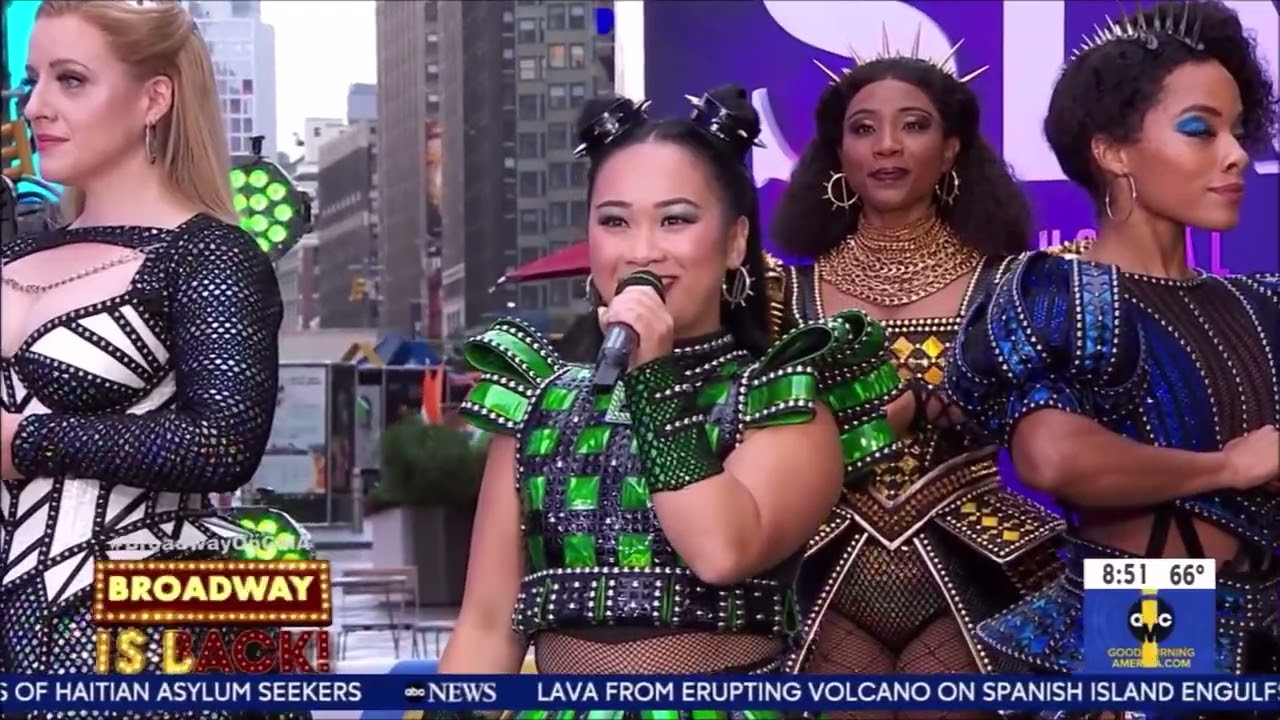
Then an undergraduate student tasked with writing an original show for the upcoming Edinburgh Festival Fringe, Marlow brought his idea to classmate Lucy Moss, who agreed to help bring his vision of a Tudor-themed pop musical to life. The product of the pair’s collaboration—Six, a modern reimagining of the lives of Henry VIII’s six wives—premiered on London’s West End in 2019 to much acclaim. (A cast soundtrack released in September 2018 similarly became an unqualified success.) Now, after an extended delay caused by the Covid-19 pandemic, the musical is finally making its Broadway debut.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/84/89/84897d27-6cf4-496e-a9ec-a51d096ab9c7/six_01_lizlauren.jpg)
Six “didn’t come out of a love of the Tudor period particularly,” says Marlow, 26. “It came from us having an interest in the representation of women in musical theater, having women on stage doing funny and hilarious things.” Moss, 27, adds, “What we were interested in doing was reframing the way that women have been perceived in history and telling their side of the story.”
The Tudor period, with its “soap opera”-esque political machinations and rich cast of female characters, offered the duo the opportunity to explore contemporary issues like feminism through a historical lens. Though Six prominently features the rhyme historically used to describe the fates of the Tudor king’s queens—“divorced, beheaded, died, divorced, beheaded, survived”—the musical moves beyond these reductive one-word summaries to present its subjects as fully realized individuals. “With all of them,” says Moss, “there was so much of interest beyond the moment they got married or divorced.”
Marlow and Moss drew on a range of sources when writing Six, including Antonia Fraser’s The Wives of Henry VIII and documentaries hosted by historian Lucy Worsley. The musical’s layered repartee deftly balances references to Tudor culture with nods to modern music, like the line “Stick around and you’ll suddenly see more” (a play on “Suddenly, Seymour” from Little Shop of Horrors). Still, Marlow explains, the show’s goal isn’t to convey history with 100 percent accuracy. Instead, “It’s [asking], ‘What if Anne Boleyn was like this?’ And how does that change the way you think about this very famous historical figure?”
Six frames its story as a makeshift talent competition in which the wife whose life was most tragic “wins.” The rules are simple: “The queen who was dealt the worst hand … shall be the one to lead the band.” Each wife sings a solo summarizing her experiences, engaging in acerbic banter in between verses. (During these numbers, the other wives act as both backup singers and dancers; beyond the six solos, the 80-minute show features three group numbers.) Ultimately, the women decide to form a girl band instead, leaving the king out of the narrative and imagining an alternate future featuring far happier ends for all of them.
Historian Jessica Storoschuk, who has written about Six extensively on her blog, has found that in school and popular culture, the queens are usually only talked about in terms of their fate. “[Six] is this kind of ridiculous satire of [that],” she says. “It’s a really intelligent way to explore their experiences, or, I should say, one part of their experiences, because their downfalls are not all of their lives.”
Below, find a song-by-song (or wife-by-wife) breakdown of the true history behind Six. Click through the interactive tools to learn more about specific lyrics from the show.
Catherine of Aragon
The song: “No Way,” a Beyoncé- and JLo-inspired “girl boss feminism” anthem, says Moss
Though Catherine of Aragon’s marriage to Henry lasted 24 years—collectively, his five other marriages spanned just 14 years—she has long been overshadowed by her successors. The daughter of Spanish monarchs Ferdinand and Isabella, Catherine came to England as the bride of Henry’s older brother, Arthur, Prince of Wales. But Arthur died shortly after the pair’s wedding, leading the Spanish princess to (eventually) marry his heir, Henry.
By all accounts, the couple enjoyed a loving relationship that only deteriorated due to a lack of a male heir and the king’s infatuation with Anne Boleyn. In the late 1520s, Henry sought a divorce from his first wife, arguing that her previous relationship with Arthur was the reason for the couple’s lack of a surviving son. Determined to protect her daughter Mary’s rights, Catherine refused to concede.
Apple News readers, click here to view this interactive.
Six’s account of these events, “No Way,” takes its cue from a June 21, 1529, meeting at Blackfriars in London. After years of debate over the validity of the royal couple’s marriage, a papal court was conceived to address the king’s so-called Great Matter. Appealing directly to her husband, Catherine fell to her knees and delivered an impassioned monologue:
Intending (as I perceive) to put me from you, I take God and all the world to witness, that I have been to you a true and humble wife, ever conformable to your will and pleasure. … If there be any just cause by the law that ye can allege against me, either of dishonesty or any other impediment to banish and put me from you, I am well content to depart, to my great shame and dishonor; and if there be none, then here I most lowly beseech you let me remain in my former estate, and receive justice at your princely hand.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/1b/ed/1bed9237-dd78-4989-8772-83e994d07e91/catherine-and-mary.jpg)
After uttering these words, Catherine left Blackfriars, ignoring the clerk’s calls for her to return. Without turning around, she declared, “On, on, it makes no matter, for it is no impartial court for me, therefore I will not tarry.” The queen was correct in her assessment: Henry had no intention of remaining in the marriage. Determined to wed Anne, he broke from the Catholic Church in order to make her his wife.
Catherine’s Six solo could’ve been a “super emotional [sad] ballad,” says Moss. Instead, she and Marlow chose to emphasize the queen’s defiance, emulating Beyoncé’s “Run the World (Girls)” and setting the tone for the rest of the musical.
The real Catherine followed through on her fictionalized counterpart’s pledge to remain “queen till the end of my life,” refusing to acknowledge her marriage’s annulment even on her deathbed in 1536. Catherine’s legacy, historian Julia Fox told Smithsonian magazine last year, “is that of a wronged woman … who did not accept defeat, who fought for what she believed to be right until the breath left her body.”
Anne Boleyn
The song: “Don’t Lose Ur Head,” a “cheeky” number modeled on Lily Allen and Kate Nash, according to Moss
Arguably the most (in)famous of the six wives, Anne is alternatively portrayed as a scheming, power-hungry seductress; a victim of her callous father’s vaulting ambition; or a worldly, charismatic woman who rose to the kingdom’s highest office only to be targeted by jealous men.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/d9/d5/d9d5f44f-89f2-444b-9ebb-96dc32698564/anneboleynhever.jpeg)
The truth of the matter depends on which scholar one asks. Most of Anne’s letters and papers were destroyed following her May 1536 execution on contrived charges of adultery, incest and conspiring to kill her husband, so much of what is known about her comes from outside observers, some of whom had reason to paint her in an unforgiving light. Even the queen’s date of birth, writes historian Antonia Fraser, is a fact “that can never be known with absolute certainty (like so much about Anne Boleyn).”
Anne’s song in Six, “Don’t Lose Ur Head,” draws its name from her method of execution: beheading by sword. Moss says she and Marlow view the number as a playful response to historians’ continued vilification of the queen as “calculating and manipulative”: “We were like, wouldn’t it be fun to mock [that trope] and make it that she was like ‘Well, I’m just living. I did this thing randomly, and now everything’s gone crazy.’”
Apple News readers, click here to view this interactive tool.
Though the tone of “Don’t Lose Ur Head” is intentionally more irreverent than the real queen, who Storoschuk says “was incredibly shrewd, very well educated, well read and well spoken,” the broad strokes of the song are historically accurate. Anne spent her teenage years in the courts of Margaret of Austria and Francis I of France, gaining a cosmopolitan worldview that helped her stand out in England. When she caught Henry’s eye, she was a maid of honor in service of his first wife; rather than becoming Henry’s mistress, as her sister Mary had, Anne refused to sleep with the king until they were married. To wed Anne, Henry broke with the Catholic Church and established himself as head of the Church of England. Finally, the once-besotted king fell out of love in dramatic—and, for Anne, fatal—fashion just three years after their long-awaited marriage.
Jane Seymour
The song: “Heart of Stone,” a slow, Adele-like ballad
Henry’s third wife, Jane Seymour, has gone down in history as the “boring” one. According to Fraser, she was intelligent and “naturally sweet-natured,” with the “salient characteristics [of] virtue and common good sense.” Historian Alison Weir similarly describes Jane as “endowed with all the qualities then thought becoming in a wife: meekness, docility and quiet dignity.”
Moss and Marlow tried to flesh out these descriptions by highlighting Jane’s political savvy. During her comparatively brief courtship with Henry, Jane drew on many of the same tactics used by Anne Boleyn, most notably by refusing to sleep with him until they were married. Presenting a submissive front may have been a tactic, says Moss. It’s also worth noting that Jane used her position to advance causes she cared about, including restoring her stepdaughters, Mary and Elizabeth, to their father’s favor and speaking out against the closure of England’s religious houses.
Apple News readers, click here to view this interactive.
On one occasion, Henry reportedly dismissed his new wife by advising her to “attend to other things, [for] the last queen had died in consequence of meddling too much in state affairs.” “Heart of Stone” acknowledges this risk, but Six’s version of Jane chooses to remain steadfast in her love of Henry and their son, the future Edward VI.
Following Jane’s death in childbirth in 1537, Henry memorialized her as “the fairest, the most discreet and the most meritorious of all his wives”—a distinction no doubt motivated by the fact that she’d given the king his only surviving male heir, writes Weir. (Edward took the throne at age 9 but died just six years later, leaving the crown to his half-sister Mary.) “Six” reflects this enviable status by identifying Jane as “the only one he truly loved.” As she herself acknowledges in “Heart of Stone,” however, Henry’s affection is conditional on her ability to provide him with a son.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/3a/7e/3a7ee89f-19af-4037-b7d9-ba3f17c9587e/2880px-family_of_henry_viii_c_1545.jpeg)
Speaking with Vulture last year, Moss said, “The idea was about the strength of choosing to love someone and committing to someone, and that being an equally valid feminist experience.” She added, “I love that [Jane] gets to say, ‘I wasn’t stupid, I wasn’t naïve.’”
Anne of Cleves
The song: “Get Down,” a 16th-century take on the rap and hip-hop “trope of being popular and bragging about your Ferrari and your Grey Goose,” says Moss
Anne (or, as the musical calls her, Anna) of Cleves was, in some historians’ view, the most successful of Henry’s six queens. After just six months of marriage, she earned the king’s enduring affection by agreeing to an annulment. Then, she proceeded to outlive her former husband, not to mention the rest of his wives, by a decade. “[Anne] did get pushed to the side in a rather unceremonious way, but she had a pretty good life,” says Storoschuk. “She was given several properties. She gambled a lot. She got to go hunting, she had the best clothes and the best food. She was loved at court.”
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/61/6c/616c8d4f-40bd-4c3e-9408-b982df0afda2/ou_sjnc_pp02-001.jpg)
“Get Down” focuses on this victorious period in Anne’s life, celebrating her independence as a wealthy, unmarried woman at Tudor court. In line with the musical’s goal of reclaiming the narrative, the number also reframes the incident that led to Anne’s annulment. Henry, enchanted by a flattering Hans Holbein portrait of his bride-to-be, was reportedly repulsed by the “tall, big-boned and strong-featured” woman who arrived in England at the beginning of 1540. Declaring “I like her not! I like her not!” after their first meeting, the king only went through with the wedding to maintain diplomatic ties with Anne’s home, the German Duchy of Cleves, and other Protestant allies across the European continent.
After just six months of marriage, Henry, eager to replace his short-reigning queen with the young, vivacious Katherine Howard, had the union annulled on the grounds of non-consummation and Anne’s pre-contract with Francis, Duke of Lorraine. Anne, from then on known as the “king’s beloved sister,” spent the rest of her days in relative luxury.
Apple News readers, click here to view this interactive.
Moss studied history at Cambridge and says much of her schoolwork centered around early modern German visual culture. Six actually includes a standalone song, “Haus of Holbein,” that satirizes 16th-century beauty culture and Henry’s portrait-driven search for a fourth wife: “Hans Holbein goes around the world / Painting all of the beautiful girls / From Spain / To France / And Germany / The king chooses one / But which one will it be?”
Given Holbein’s reputation for accuracy and Henry’s own declining looks (at the time of the couple’s wedding, the king was 48 years old), Marlow and Moss chose to turn the tables, having Anne proclaim herself a fan of the much-vilified portrait. Further cementing Anne’s mastery of the situation, “Get Down”’s refrain finds the supposedly unattractive queen hanging up her likeness “for everyone to see.”
Katherine Howard
The song: “All You Wanna Do,” a catchy number modeled on the work of “young pop stars sexualized early on in their careers,” like Miley Cyrus, Britney Spears and Ariana Grande, as Marlow told Vulture
For much of history, Henry’s fifth wife, Katherine Howard, has been dismissed as a wanton woman of little import. Writing in 1991, Weir described her as a “frivolous, empty-headed young girl who cared for little else but dancing and pretty clothes.” Fraser, meanwhile, wrote that “[h]ere was no intelligent adult woman, wise in the ways of the world—and of course courts.” More recent scholarship has taken a sympathetic view of the queen, with Gareth Russell’s 2017 book, Young and Damned and Fair, leading the conversation. As Russell argues, “[Katherine] was toppled by a combination of bad luck, poor decisions and the Henrician state’s determination to punish those who failed its king.”
Katherine’s Six solo, titled “All You Wanna Do,” echoes Russell’s characterization of its subject as a victim of circumstance and predatory older men. Though her exact birthdate is unknown, Katherine may have been as young as 17 when she was beheaded on charges of treasonous adultery in February 1542. Henry, comparatively, was almost 50 at the time of his disgraced wife’s execution.
Apple News readers, click here to view this interactive.
The king was far from the first man to sexualize Katherine. “All You Wanna Do” details the queen’s relationships in heart-wrenching detail, from a liaison with her music teacher, Henry Manox (the song suggests that he was 23 to Katherine’s 13, but as Storoschuk points out, he may have been closer to 33), to an affair with Francis Dereham, secretary to the dowager duchess, Katherine’s step-grandmother. When each new romance begins, the teenager declares herself hopeful that this time will be different. By the end of the song, however, she realizes that all of her suitors have the same goal in mind.
According to Moss, she and Marlow wanted Katherine’s song to start out with a “sexy, seductive” tone before transforming into a “narrative of abuse” with echoes of today’s #MeToo movement. Marlow adds, “It was kind of like us talking about what happened to one of the queens and finding a way of relating it to something that we would recognize as a modern female experience.”
Katherine’s “life was so tragic,” says Storoschuk. “She was so young, and she really had very little agency over her own life. ‘All You Wanna Do’ really encompasses that.”
Catherine Parr
The song: “I Don’t Need Your Love,” a soulful, Alicia Keys–inspired love song
Often reduced to the one-word summary of “survived” or the role of nursemaid to a succession of ailing husbands, Henry’s sixth wife, Catherine Parr, was actually a renowned scholar, religious reformer and perhaps even protofeminist. In Six, she takes ownership of these attributes, refusing to be defined by her romantic relationships and instead listing her manifold accomplishments: “Remember that I was a writer / I wrote books and psalms and meditations / Fought for female education / So all my women can independently study scripture / I even got a woman to paint my picture.”
Apple News readers, click here to view this interactive.
As the last of the six to take the stage, the fictionalized Catherine has dual obligations: namely, sharing her story and setting up a satisfying musical finale. “We needed one of the queens to be like ‘Wait, we shouldn’t be competing with each other. We should support each other,’” says Moss. “Fortunately, [Catherine’s role] as a writer, educator and advocate for women helped with that.” Encouraging the wives to take back the microphone, Catherine calls for them to assert themselves outside of their marriages to Henry. “It’s not what went down in history,” the six admit, “[b]ut tonight, I’m singing this for me.”
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/f7/f1/f7f1a2dc-3983-4346-93c4-c048316668c3/1280px-thomas_seymour_denizot.jpeg)
The real Catherine led a rich life beyond what’s captured in “I Don’t Need Your Love.” As alluded to by the song’s first verses, which find Catherine telling a lover that she has “no choice” but to marry the king, the twice-married young widow initially had another suitor in mind: Thomas Seymour, the dashing younger brother of Henry’s third wife, Jane. (The would-be couple wed soon after Henry’s death in 1547, but their marriage was tainted by Thomas’ improper conduct toward his new stepdaughter, the future Elizabeth I.)
Despite being forced into a relationship with Henry, Catherine made the most of her position, pushing her husband to embrace Protestantism and encouraging him to restore his daughters to the line of succession. She narrowly escaped an attempt by the court’s conservative faction to have her executed on charges of heresy, winning back Henry’s favor even after he’d signed a warrant for her arrest. Catherine died just a year after the king, succumbing to complications from childbirth in 1548.
:focal(647x413:648x414)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/fa/9e/fa9ea364-f2da-4f49-bced-5b676a5c36a4/six-lead.jpg)
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/mellon.png)


/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/mellon.png)