In recent years, curators and educators have increasingly started exploring the many possibilities offered by virtual exhibitions. Hundreds of institutions have made 3-D tours of their galleries available online through Google Arts & Culture and similar platforms, allowing visitors from around the world to virtually “wander” through the Van Gogh Museum in Amsterdam, Frida Kahlo’s Casa Azul in Mexico City, the Tokyo National Museum and other significant sites.
But when the Covid-19 pandemic forced museums to shutter for most of 2020, public interest in virtual art experiences skyrocketed like never before. Closed to the public and financially strained, many museums nevertheless managed to create thought-provoking alternatives to in-person viewing.
Digital offerings in the United States ranged from the Morgan Library & Museum’s interactive retrospective of Al Taylor’s drawings to the Museum of Modern Art’s (MoMA) “Virtual Views” of Surrealist women. Abroad, exhibitions such as the Rijksmuseum’s interactive version of a Rembrandt masterpiece offered viewers a chance to literally “zoom in” on a single piece of art—and perhaps notice new details that would’ve otherwise gone unnoticed. In London, meanwhile, Tate Modern adapted its “Andy Warhol” show by creating a curator-led tour that takes users through the exhibition room by room.
The Smithsonian Institution also made impressive forays into the world of online exhibitions. A beautifully illustrated portal created by the National Museum of American History and the Smithsonian American Women’s History Initiative examined how girls have shaped history, while a landmark show at the Smithsonian American Art Museum spotlighted Chicano activists’ pioneering printmaking. At the National Museum of Natural History, curators catered to science enthusiasts with narrated virtual tours of various exhibits and halls; at the National Air and Space Museum, aviation experts produced panoramic views of famed aircrafts' interiors. Other highlights included the National Museum of Asian Art’s virtual reality tour of six iconic monuments from across the Arab world, the Cooper Hewitt’s walkthrough of “Contemporary Muslim Fashions,” and the National Museum of African American History and Culture’s exploration of black soldiers’ experiences during World War I. (For a more complete list of offerings, visit the Smithsonian’s online exhibitions portal.)
To mark the end of an unprecedented year, Smithsonian magazine is highlighting some of the most innovative ways in which museums helped craft meaningful virtual encounters with history and art. From first ladies to women writers and Mexican muralists, these were ten of our favorite online exhibitions of 2020.
“Every Eye Is Upon Me: First Ladies of the United States”
The Smithsonian’s National Portrait Gallery (Washington, D.C.)
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/fe/71/fe719aff-9840-45a8-a410-664389f05bf3/first_laides3.jpg)
Visitors to the National Portrait Gallery’s presidential wing have long called for an exhibition devoted to the U.S.’ first ladies. But as Alicia Ault points out for Smithsonian, these women haven’t always been recognized as important individuals in their own right—a fact reflected in the relative dearth of portraiture depicting them. The gallery itself only began commissioning official portraits of the first ladies in 2006.
“Every Eye Is Upon Me: First Ladies of the United States” seeks to redress this imbalance by presenting 60 portraits—including photographs, drawings, silhouettes, paintings and sculptures—of American presidents’ wives. Though the physical exhibition is currently closed due to the Covid-19 pandemic, would-be visitors can explore a virtual version featuring high-resolution images of first ladies from Martha Washington to Melania Trump, as well as brief biographies, podcasts and blog posts. The portraits are as “varied as the women themselves,” who all responded to the unique challenges and pressures of their office in different ways, writes Ault.
Inspiration for the exhibition’s title comes from Julia Gardiner, who was the first woman to marry a president in office. Born into a wealthy Long Island slaveholding family, Gardiner was just 24 years old when she wed John Tyler in 1844. As Gardiner prepared to take on the high-profile role, she wrote in a letter to her mother that she knew she would be scrutinized: “I very well know every eye is upon me, my dear mother, and I will behave accordingly.”
“Jacob Lawrence: The American Struggle”
Peabody Essex Museum (Salem, Massachusetts)
One of black history’s preeminent visual storytellers, Jacob Lawrence employed Modernist forms and bright colors to narrate the American experience through the eyes of the country’s most marginalized citizens. This year, the Peabody Essex Museum in Salem, Massachusetts, reunited one of Lawrence’s most groundbreaking series—Struggle: From the History of the American People (1954–56)—for the first time in 60 years.
In 30 hardboard panels, each measuring 12 by 16 inches, Lawrence traces American history from the Revolutionary War to 1817, covering such events as the Boston Tea Party and the nation’s bloody, prolonged campaigns against Native Americans, as Amy Crawford wrote for Smithsonian in June. Virtual visitors can stroll through the exhibition, aptly titled “Jacob Lawrence: The American Struggle,” or zoom in on images of each panel. Entries are accompanied by related artworks and reflections from scholars.
When the show traveled to the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, it sparked an exciting reunion. A museum visitor recognized the panels’ distinct Modernist style and realized that her neighbors, a couple living on the Upper West Side, had a similar painting hanging in their living room. Curators determined that the panel, which depicts Shay’s Rebellion, was one of five missing works from the Struggle series. No photographs of the panel had survived, and it had been presumed lost for decades—but as curator Randall Griffey told the New York Times, it turned out to be “just across the park” from the museum.
“Vida Americana: Mexican Muralists Remake American Art, 1925–1945”
Whitney Museum of American Art (New York City)
When the Mexican Revolution drew to a close in 1920 after ten years of armed struggle, the country was left profoundly changed. But among artists of the post-revolutionary period, a new cultural revolution was just beginning. Over the next several decades, artists like the famed Tres Grandes, or Big Three—José Clemente Orozco, Diego Rivera and David Alfaro Siqueiros—started crafting radical, large-scale works that embraced Mexico’s Indigenous cultures and told epic narratives about the nation’s history.
As “Vida Americana,” an ongoing exhibition at the Whitney Museum of American Art, argues, these sweeping, dynamic murals also had a major impact on Mexico’s neighbors to the north. As Mexican artists traveled to the U.S. (and vice versa), they taught their peers how to break free of European conventions and create public art that celebrated American history and everyday life. On the show’s well-organized online hub, art lovers can explore short documentaries, audio guides, essays and other resources in both Spanish and English. Click through some of the selected artworks from the show to encounter Rivera’s Detroit Institute of Art masterpiece, a massive 27-mural cycle that offered Americans reeling from the Great Depression a visionary outlook of their country’s future industrial potential, and Siqueiros’ experimental workshop, which directly inspired Jackson Pollock’s Abstract Expressionism.
“Dorothea Lange: Words & Pictures”
The Museum of Modern Art (New York City)
Recognized today as one of America’s foremost photographers, Dorothea Lange is known for her arresting portraits of the human condition and keen social awareness—qualities perhaps best exemplified by her 1936 image Migrant Mother, which became a de facto symbol of the Great Depression.
But few people know that Lange was also enamored with the written word. As she once said, “All photographs—not only those that are so called ‘documentary’... can be fortified by words.” Lange believed that words could clarify and add context to photographs, thereby strengthening their social impact. In her landmark photobook An American Exodus: A Record of Human Erosion, she became one of the first photographers to incorporate her subject’s own words into her captions, as Smithsonian reported in August.
Through this MoMA exhibition’s online hub, viewers can read selections of Lange’s writing, watch a series of short videos on her work, listen to interviews with curator Sarah Meister, and—of course—take their time studying close-up versions of the artist’s iconic photographs.
“Writing the Future: Basquiat and the Hip-Hop Generation”
Museum of Fine Art, Boston (Boston, Massachusetts)
Jean-Michel Basquiat is often touted as a singular genius. His large-scale works, which riff on color, phrases and iconography to probe issues of colonialism, racism and celebrity, regularly fetch enormous sums at auction.
But the graffiti artist–turned–painter, who died of a heroin overdose at age 27, didn’t develop his artistic vision in a vacuum: Instead, he was profoundly influenced by a network of peers and close collaborators. “Writing the Future: Basquiat and the Hip-Hop Generation,” which opened at the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, in October, is the first show to consider the influence of Basquiat’s large circle of mainly black and Latino collaborators, all of whom shaped the painter’s artistic vision in 1980s New York City.
The museum complemented its in-person show with a multimedia-heavy online exhibition, which includes detailed essays, images of works in the show and clips of interviews with the artist. Viewers are encouraged to scour lesser-known artworks from Basquiat’s peers, such as the “Gothic futurist” paintings of Rammellzee and the rebellious murals of Lady Pink, in search of themes and styles that Basquiat echoed in his own work.
“Making the Met, 1870–2020”
Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York City)
A group of businessmen and civic leaders purchased the Metropolitan Museum of Art’s first work—a marble sarcophagus from ancient Rome—in 1870. Since then, the museum’s collections have become some of the greatest troves of cultural heritage in the world, constituting an encyclopedic range of artifacts that attracts millions of visitors each year.
This year, the Manhattan museum celebrated its 150th birthday by hosting a celebratory exhibition and slate of virtual offerings: Among others, the list of digital resources includes an hour-long audio tour of some of the exhibition’s highlights, as narrated by actor Steve Martin; an interactive online version of the show; and a virtual walkthrough courtesy of Google Arts and Culture. Met officials also made a rare gem available for public viewing: Behind the Scenes: The Working Side of the Museum, a silent 1928 documentary that depicts curators and janitors at work in the iconic New York building.
“The Museum of the World”
The British Museum (London, England)
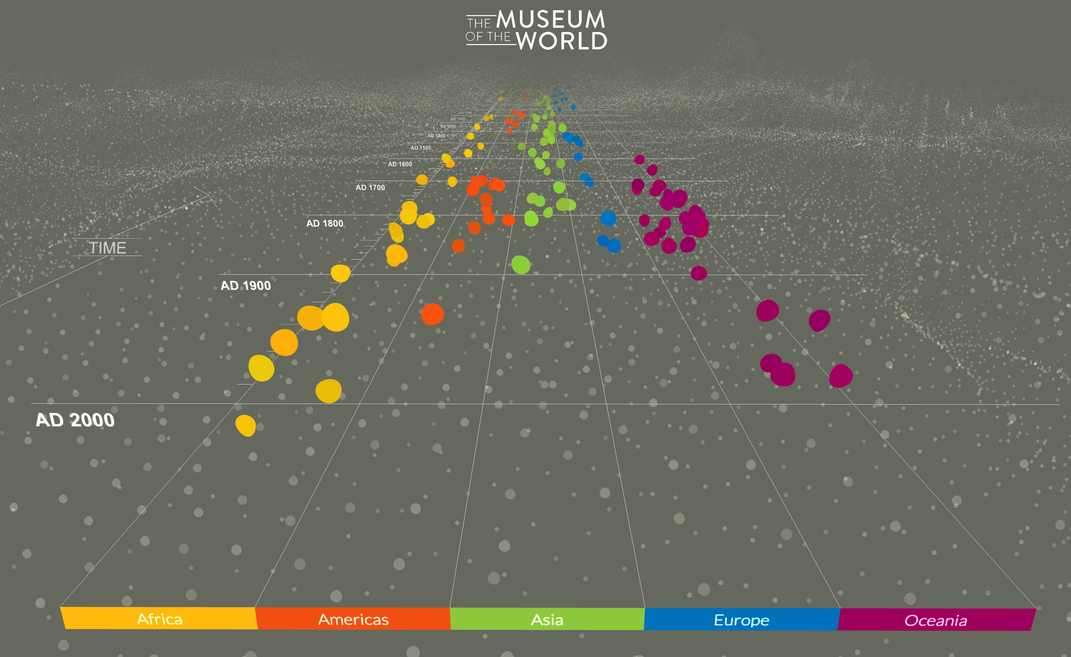
An innovative example of the possibilities of online exhibitions, the British Museum’s “Museum of the World” debuted in February 2020—and it couldn’t have been better timed. Though the museum remained closed to in-person visitors for much of the year, desktop computer users were able to use this interactive timeline to visualize connections between different items in the museum’s vast collections.
On the website, which the museum developed in partnership with Google Arts & Culture, viewers can trace links through time and space, jumping from a handscroll describing courtly behavior of ladies in the Eastern Jin Dynasty of China to the jade plaque of a Maya king. With a slick interface and audio elements, the timeline encourages viewers to take an interactive, self-directed trip through the material culture of human history.
Notably absent from the project is an acknowledgement of the London museum’s colonialist history, which came under renewed scrutiny this summer amid global protests against systemic racism. In August, the cultural institution moved a bust of its founder, who profited from the enslavement of people in Jamaica, to a new display featuring added contextualization. As Aditya Iyer writes for Hyperallergic, the museum recently made a “promising but flawed start [at] grappling with” this legacy by curating a self-guided tour titled “Empire and Collecting.” Available online in an abbreviated format, the tour traces the “different, complex and sometimes controversial journeys of objects” that entered the collections, according to the museum's website.
“The Night Watch”
The Rijksmuseum (Amsterdam, the Netherlands)
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/f8/50/f850e5e0-f38a-4a11-85c8-5d2748ce64f8/screen_shot_2020-12-30_at_42200_pm.png)
In this new hyper-resolution view of Rembrandt van Rijn’s The Night Watch, art lovers can pore over every detail of the Dutch master’s most famous painting—down to every crack and stray paint splatter, as Theresa Machemer wrote for Smithsonian in May. The Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam debuted the interactive version of its prized painting as part of a lengthy restoration process dubbed Operation Night Watch. Last year, experts began restoring the 11- by 15-foot painting in a glass chamber installed in the middle of the museum, offering visitors a rare behind-the-scenes glimpse at the conservation process.
Officially titled Night Watch, Militia Company of District II under the Command of Captain Frans Banninck Cocq, the 1642 painting depicts a captain instructing a cadre of soldiers. In the online guided tour (which comes with options for children and adults), users can zoom in on different aspects of the painting while a soundscape—the swish of a cloak, a horse’s hooves, an eerie melody, a far-off bell—sets the mood. Look for Rembrandt’s signature, his presumed self-portrait lurking in the painting’s background, the striking young girl with a chicken dangling from her belt and other mysterious elements embedded in the action-packed scene.
According to a statement, the image combines 528 exposures into one composite, making it the most detailed rendering of Rembrandt’s masterpiece ever created. The project is a prime example of how online galleries can encourage viewers to engage in repeated, close study of the same piece of art—and proof that they can always discover something new.
“Van Eyck: An Optical Revolution”
Museum of Fine Arts Ghent (Ghent, Belgium)
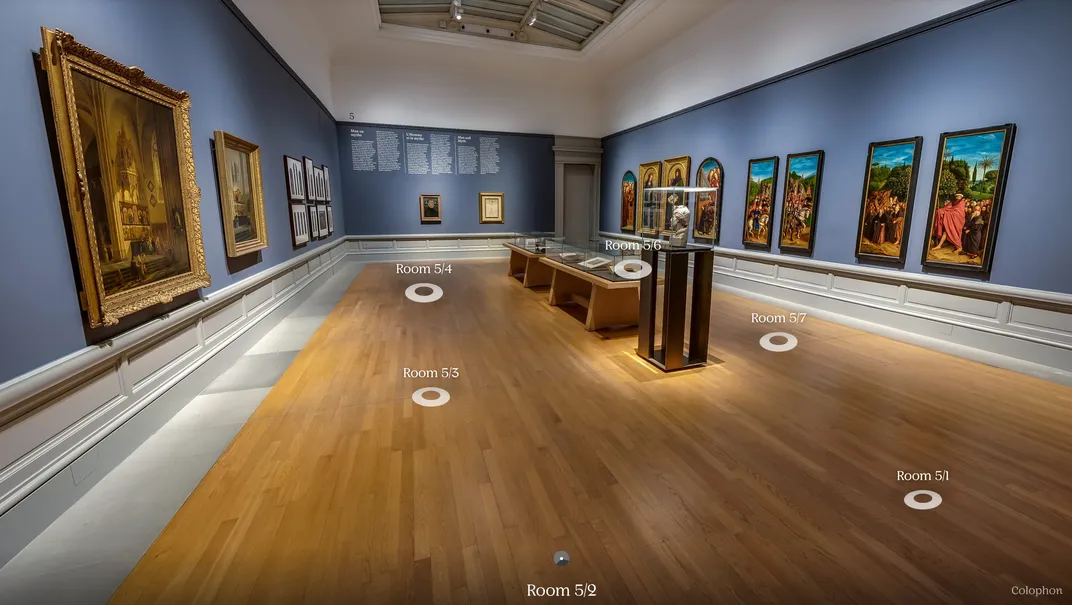

Curators and art enthusiasts were crushed when the pandemic forced a blockbuster Jan van Eyck exhibition at the Museum of Fine Arts in Ghent to close less than two months after opening. The once-in-a-generation show—titled “Van Eyck: An Optical Revolution”—represented the largest-ever display of van Eyck’s paintings and was “so unlikely to be repeated that the museum might as well use ’now or never,’” as J.S. Marcus wrote for the Wall Street Journal in January.
In response to the unexpected closure, the museum pivoted, partnering with Belgian virtual reality company Poppr to create a 360-degree tour of the gallery with accompanying audio guides for adults and children. Star items featured in the show included Portrait of a Man (Léal Souvenir) and panels from the spectacular Ghent Altarpiece, whose center panel depicts Jesus as a sacrificial lamb on an altar, alive but bleeding from a wound. Prior to the exhibition, the panels had not left their home in St. Bavo’s Cathedral since 1945, as Sophie Haigney reported for the New York Times earlier this year.
Born in 1390 in what is now Belgium, van Eyck created spectacularly detailed oil paintings of religious scenes. As the show’s website notes, only about 20 of the Flemish master’s paintings survive today.
“Wise and Valiant: Women and Writing in the Golden Age of Spain”
Instituto Cervantes (Madrid, Spain)
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/cf/f5/cff5e283-35ca-4eef-ad4b-1018d175536c/screen_shot_2020-12-30_at_43411_pm.png)
Spain’s Golden Age is perhaps best known for producing Miguel Cervantes’ Don Quixote, El Greco’s eerily elongated portraits and Lope de Vega’s prolific plays. But as the now-closed exhibition “Wise and Valiant” showed, these individuals and their male peers weren’t the only creative geniuses at work during the 16th and 17th centuries. Though women’s opportunities at the time were largely limited to the domestic and religious spheres, a select few took advantage of the relative intellectual freedom offered by life in a convent to pursue writing professionally.
From Mexican nun Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz to playwright Ana Caro and nun-turned-soldier Catalina de Erauso, hundreds of women across the Spanish Empire published poetry, diaries, novels, dramatic works and travelogues. Though many of these works have since been lost or forgotten, scholars are increasingly taking steps to recover their authors’ hidden stories—a trend reflected in the Madrid show, which explored women writers’ lives through a display of more than 40 documents. As Lauren Moya Ford observed in Hyperallergic’s review of the show, the online version of the exhibition (available in both Spanish and English) presents their stories in a “format well-suited to this dense, delicate material.” Users can delve into digitized historical documents, browse curator commentary and watch a video montage of relevant clips.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/c0/9a/c09afabd-94f6-4ef6-8a00-0fcf4d8f0f9d/online_exhibitions_mobile.jpg)
:focal(980x333:981x334)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/37/97/37976aff-f4ff-469b-89c5-284f89f0a46c/online_exhibitions_longform2.jpg)
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/nora.png)





/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/nora.png)