A 3.8-Million-Year-Old Skull Puts a New Face on a Little-Known Human Ancestor
The cranium of a male Australopithecus anamensis, a close relative of Lucy, provides clues about one of the earliest hominins to walk on two legs
:focal(1000x666:1001x667)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/af/09/af094262-6126-4543-9707-49eba5234d84/clippedfront.jpg)
Spotting the intact Australopithecus skull in the Ethiopian dirt caused paleoanthropologist Yohannes Haile-Selassie to literally jump for joy. “It was something that I’ve never seen before, and I’ve seen a lot of cranial fossils,” he says.
The chance discovery by Haile-Selassie and an Ethiopian shepherd has created a captivating portrait of 3.8-million-year-old face, providing an unprecedented look at a hominin species from a key stage of human evolution. Experts say the extraordinary fossil can help redefine the branches of humans’ evolutionary tree during a time when our ancestors had just evolved efficient ways to walk upright.
“This cranium looks set to become another celebrated icon of human evolution,” Fred Spoor, a human evolution researcher at the Natural History Museum in London, writes in a News & Views article that accompanied Haile-Selassie and colleagues’ new study in the journal Nature.
The amazingly complete skull surfaced at Woranso-Mille, in Ethiopia’s Afar region, back in 2016. But it has taken 3 and a half years of hard work to answer the first question that arose—just what kind of skull is it?
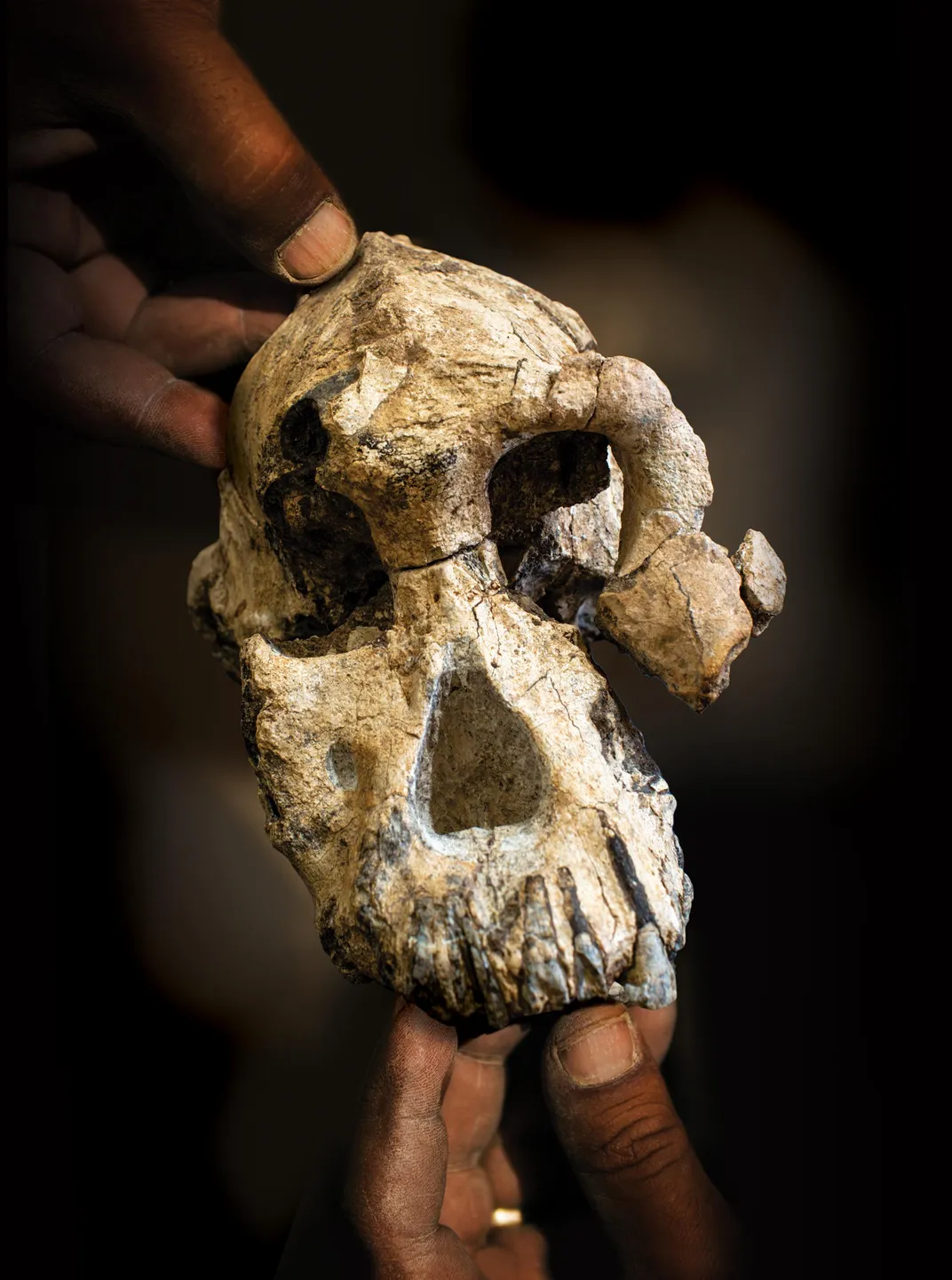
Haile-Selassie and colleagues compared the skull (dubbed MRD after part of its collection ID number) with a wide variety of hominin fossils from across Africa. They sized up different morphological features to see what species the cranium represents and where it fits in the interconnected lineages of our family tree. The results identify the skull as belonging to a male Australopithecus anamensis. The hominin species is theorized to have vanished a bit earlier than 3.8 million years ago after giving rise to a later lineage, Australopithecus afarensis, to which the famed fossil Lucy belongs. A. anamensis has traits of both apes (climbing arms and wrists) and humans (changes in the ankles and knee joints to facilitate walking on two feet).
Most previous fossil specimens of A. anamensis are limited to small bits of bone, such as a tooth, partial jaw, or fragment of arm or shin. The opportunity to study a nearly complete braincase and face confirms the “southern ape” as a unique species and shines light on the differences between two of our most ancient hominin ancestors, A. anamensis and A. afarensis.
“Most of A. anamensis’ own traits are quite primitive,” Haile-Selassie says, noting the individual’s small brain, protruding face and large canine teeth. “There are a few features exclusively shared with A. afarensis, like the orbital region in the frontal area. But everything else is really primitive. If you look at it from the back, it looks like an ape. This is something that I never expected to see in a species that is hypothesized to be the ancestor of A. afarensis. So it changed the whole gamut of ideas in terms of the relationship between those two.”
The skull also casts doubt on prevailing ideas that the older lineage directly gave rise to the younger, instead suggesting that the two lived together, coexisting for at least 100,000 years. But the study authors stress that it’s still quite possible that early populations of A. anamensis gave rise to A. afarensis perhaps 4 million years ago—they just didn’t die out immediately afterwards.
“Probably a small population of A. anamensis isolated itself from the main population, underwent major changes, and over time distinguished itself from the parent species of A. anamensis. That’s probably how A. afarensis appeared,” Haile-Selassie says.
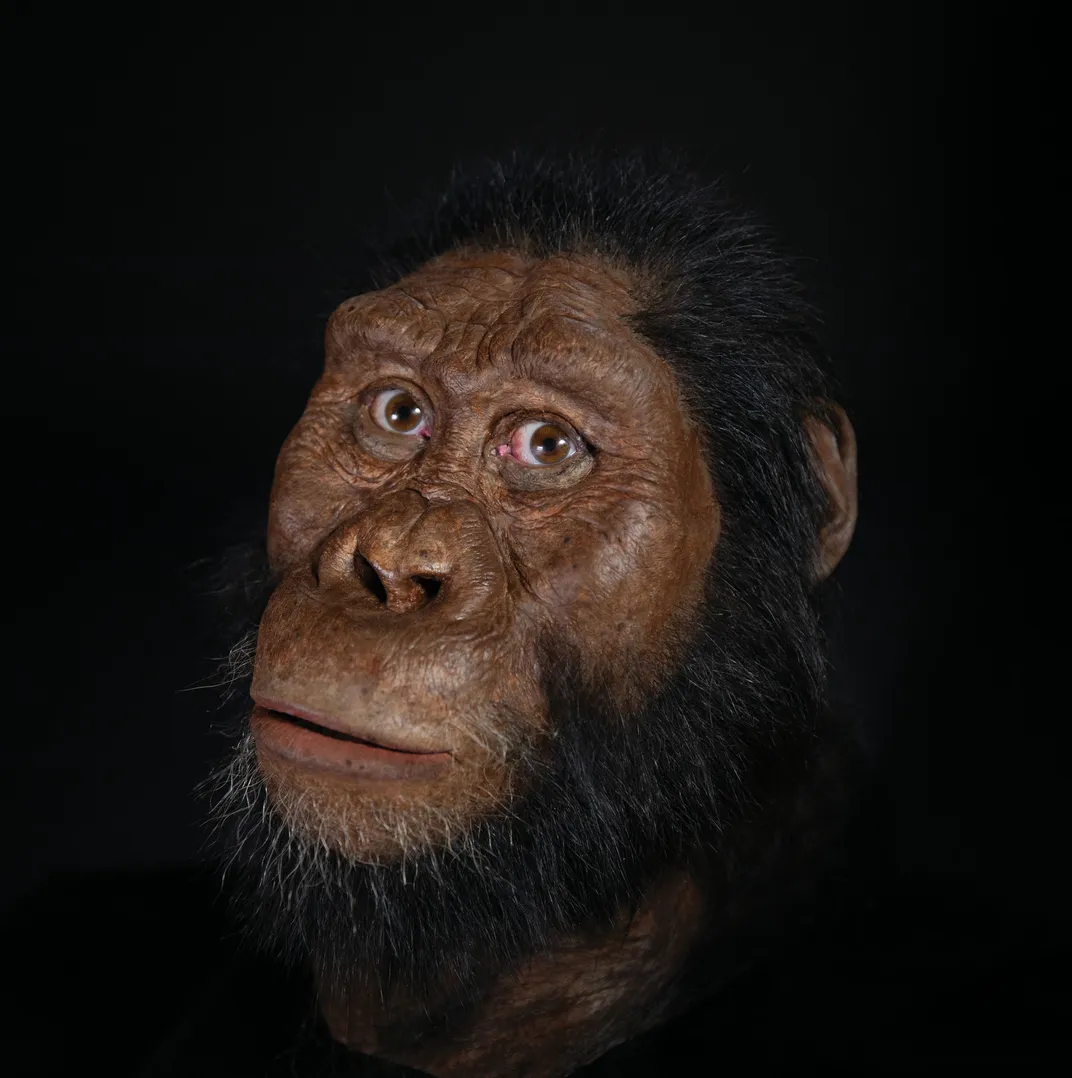

The research team argues that the relationship between the two ancient hominin species, believed to be ancestors to our own genus Homo, may be a prime example of a nonlinear evolutionary scenario common in other non-human species. Anagenesis, when one species evolves so completely into another species that the progenitor disappears, is not the primary way the branches on our family tree diverged.
“Just because one species gave rise to another, it doesn’t mean that the source species (ancestor) disappeared,” Rick Potts, head of the Smithsonian’s Human Origins Program who was not involved in the new study, says via email from a dig in Kenya. “We’ve known for some time that the human family tree is branching and diverse, like the evolutionary trees of almost all other species. The new cranium is significant because it illustrates this pattern of biodiversity in a poorly known period of hominin evolution, just as our ancestors evolved a stronger and stronger commitment to walking on two legs.”
Paleoanthropologist Meave Leakey and colleagues reported in 1995 that A. anamensis was the first known species to evolve an expanded knee joint that allowed each of its legs to briefly bear all of its body weight during bipedal walking. Bipedalism set our ancestors apart from the apes, enabling ancient hominins to take advantage of a wider range of habitats than those available to tree climbers.
A second, related study helped to more precisely date the cranium fossil by investigating minerals and volcanic layers where it was found. The work also helped describe the long-vanished world in which A. anamensis and his kin lived.
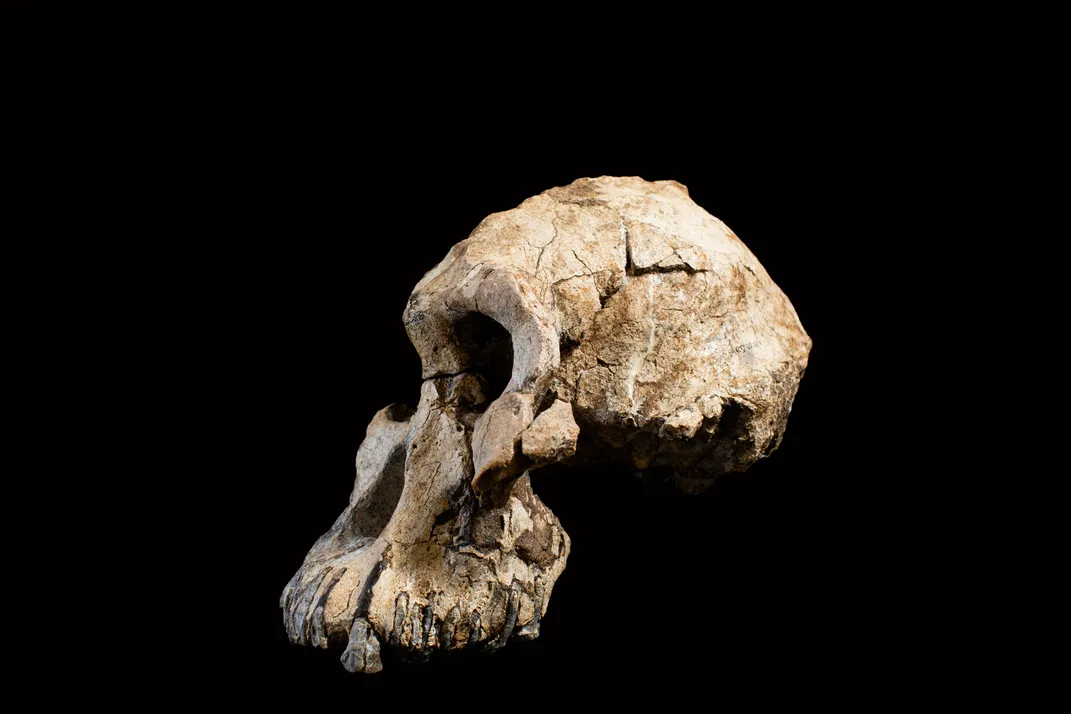

The skull was buried in sand that was deposited in a river delta on the shores of an ancient lake. The sediment deposits also held botanical remains, revealing that the environment around the ancient lake was predominantly dry shrubland, but there was a mixture of other local ecosystems as well.
“There were forests around the shores of the lake and along the river that flowed into it, but the surrounding area was dry with few trees,” Beverly Saylor, a geologist at Case Western Reserve University and lead author of the second study, said at a press conference. The evidence suggests that, like contemporaries from other sites, the male hominin likely dined on a tough, ape-like diet of seeds, grasses and similar fare.
Haile-Selassie and colleagues have been working in the area of Woranso-Mille, Ethiopia, for 15 years. When a local shepherd showed up in camp to announce the find of some intriguing fossils, Haile-Selassie was skeptical, especially because locals had often dragged him to visit supposed fossil sites simply because they needed a ride somewhere. He asked Habib Wogris, the local chief who organizes fieldwork in the region each year, to take an hour-long walk with the shepherd to visit the site of his find.
“The chief has seen a lot of teeth of hominins from the site and he realized that this tooth looked like a hominin tooth,” Haile-Selassie says. “As soon as he returned and opened his hand and I saw the tooth, I said, ‘Where did you find it?’ They said, ‘let’s go and we'll show you.’”
The fossil site was in the region’s high ground, where the shepherd had moved his flock to escape seasonal flooding in lower areas. “He’s been living there like three months with his goats, and he saw the fossil when he was digging a hole for his newborn goats to make a protection for them from jackals and hyenas,” Haile-Selassie says.
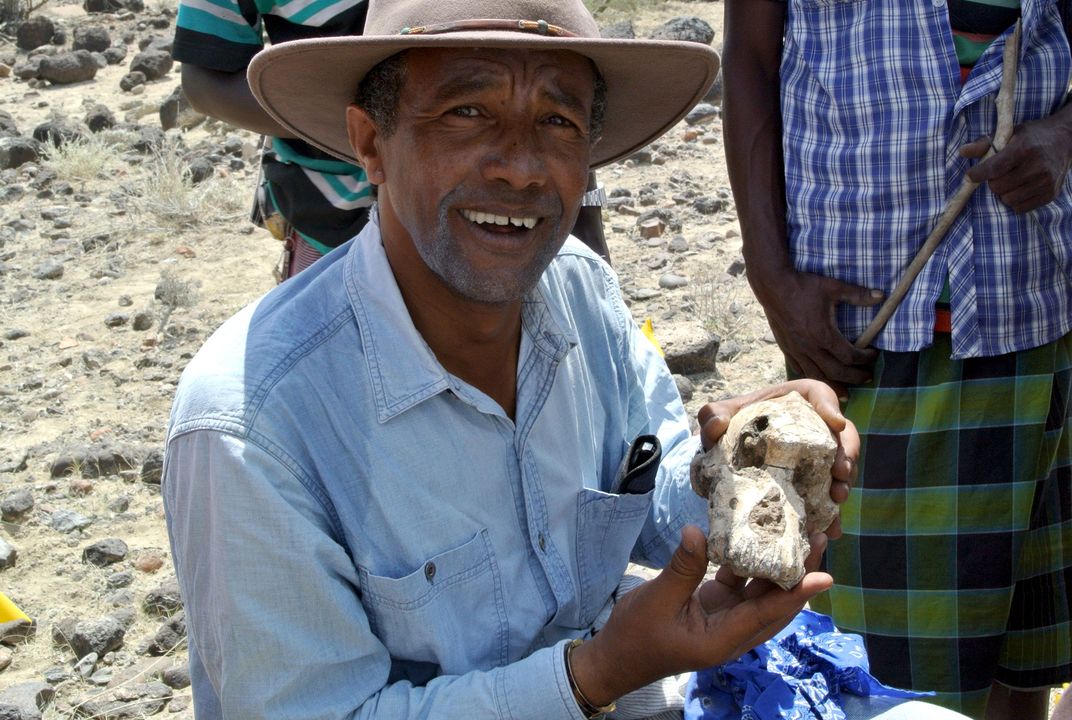

On site, the shepherd showed him where the tooth had been lying, and Haile-Selassie surveyed the surroundings looking for other fragments.
“Three meters from where I was standing there was this round thing, just like a rock, and I said oh my goodness,” Haile-Selassie’s recalls. His reaction, literally jumping up and down with excitement, made the shepherd remark that the doctor had gone crazy. “I speak their language, and I said no the doctor is not going crazy. He’s just excited,” Haile-Selassie laughs.
With the rare fossil’s formal unveiling today, the excitement of the initial find three years ago has spread throughout the community of scientists looking to put a human, or hominin, face on our distant ancestors.