The Ten Most Disturbing Scientific Discoveries
Scientists have come to some surprising conclusions about the world and our place in it. Are some things just better left unknown?
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/polar-bear-glaciers-climate-control-631.jpg)
Science can be glorious; it can bring clarity to a chaotic world. But big scientific discoveries are by nature counterintuitive and sometimes shocking. Here are ten of the biggest threats to our peace of mind.
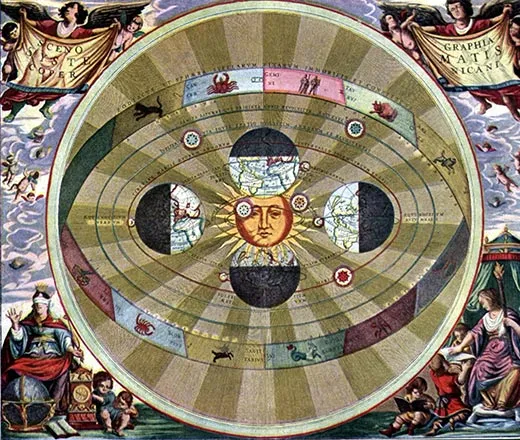
1. The Earth is not the center of the universe.
We’ve had more than 400 years to get used to the idea, but it’s still a little unsettling. Anyone can plainly see that the Sun and stars rise in the east, sweep across the sky and set in the west; the Earth feels stable and stationary. When Copernicus proposed that the Earth and other planets instead orbit the Sun,
… his contemporaries found his massive logical leap “patently absurd,” says Owen Gingerich of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. “It would take several generations to sink in. Very few scholars saw it as a real description of the universe.”
Galileo got more grief for the idea than Copernicus did. He used a telescope to provide evidence for the heliocentric theory, and some of his contemporaries were so disturbed by what the new invention revealed—craters on a supposedly perfectly spherical moon, other moons circling Jupiter—that they refused to look through the device. More dangerous than defying common sense, though, was Galileo’s defiance of the Catholic Church. Scripture said that the Sun revolved around the Earth, and the Holy Office of the Inquisition found Galileo guilty of heresy for saying otherwise.
2. The microbes are gaining on us.
Antibiotics and vaccines have saved millions of lives; without these wonders of modern medicine, many of us would have died in childhood of polio, mumps or smallpox. But some microbes are evolving faster than we can find ways to fight them.
The influenza virus mutates so quickly that last year’s vaccination is usually ineffective against this year’s bug. Hospitals are infested with antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus bacteria that can turn a small cut into a limb- or life-threatening infection. And new diseases keep jumping from animals to humans—ebola from apes, SARS from masked palm civets, hantavirus from rodents, bird flu from birds, swine flu from swine. Even tuberculosis, the disease that killed Frederic Chopin and Henry David Thoreau, is making a comeback, in part because some strains of the bacterium have developed multi-drug resistance. Even in the 21st century, it’s quite possible to die of consumption.
3. There have been mass extinctions in the past, and we’re probably in one now.
Paleontologists have identified five points in Earth’s history when, for whatever reason (asteroid impact, volcanic eruptions and atmospheric changes are the main suspects), mass extinctions eliminated many or most species.
The concept of extinction took a while to sink in. Thomas Jefferson saw mastodon bones from Kentucky, for example, and concluded that the giant animals must still be living somewhere in the interior of the continent. He asked Lewis and Clark to keep an eye out for them.
Today, according to many biologists, we’re in the midst of a sixth great extinction. Mastodons may have been some of the earliest victims. As humans moved from continent to continent, large animals that had thrived for millions of years began to disappear—mastodons in North America, giant kangaroos in Australia, dwarf elephants in Europe. Whatever the cause of this early wave of extinctions, humans are driving modern extinctions by hunting, destroying habitat, introducing invasive species and inadvertently spreading diseases.
4. Things that taste good are bad for you.
In 1948, the Framingham Heart Study enrolled more than 5,000 residents of Framingham, Massachusetts, to participate in a long-term study of risk factors for heart disease. (Very long term—the study is now enrolling the grandchildren of the original volunteers.) It and subsequent ambitious and painstaking epidemiological studies have shown that one’s risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes, certain kinds of cancer and other health problems increases in a dose-dependent manner upon exposure to delicious food. Steak, salty French fries, eggs Benedict, triple-fudge brownies with whipped cream—turns out they’re killers. Sure, some tasty things are healthy—blueberries, snow peas, nuts and maybe even (oh, please) red wine. But on balance, human taste preferences evolved during times of scarcity, when it made sense for our hunter-gatherer ancestors to gorge on as much salt and fat and sugar as possible. In the age of Hostess pies and sedentary lifestyles, those cravings aren’t so adaptive.
5. E=mc²
Einstein’s famous equation is certainly one of the most brilliant and beautiful scientific discoveries—but it’s also one of the most disturbing. The power explained by the equation really rests in the c², or the speed of light (186,282 miles per second) times itself, which equals 34,700,983,524. When that’s your multiplier, you don’t need much mass—a smidgen of plutonium is plenty—to create enough energy to destroy a city.
6. Your mind is not your own.
Freud might have been wrong in the details, but one of his main ideas—that a lot of our behaviors and beliefs and emotions are driven by factors we are unaware of—turns out to be correct. If you’re in a happy, optimistic, ambitious mood, check the weather. Sunny days make people happier and more helpful. In a taste test, you’re likely to have a strong preference for the first sample you taste—even if all of the samples are identical. The more often you see a person or an object, the more you’ll like it. Mating decisions are based partly on smell. Our cognitive failings are legion: we take a few anecdotes and make incorrect generalizations, we misinterpret information to support our preconceptions, and we’re easily distracted or swayed by irrelevant details. And what we think of as memories are merely stories we tell ourselves anew each time we recall an event. That’s true even for flashbulb memories, the ones that feel as though they’ve been burned into the brain:
Like millions of people, [neuroscientist Karim] Nader has vivid and emotional memories of the September 11, 2001, attacks and their aftermath. But as an expert on memory, and, in particular, on the malleability of memory, he knows better than to fully trust his recollections… As clear and detailed as these memories feel, psychologists find they are surprisingly inaccurate.
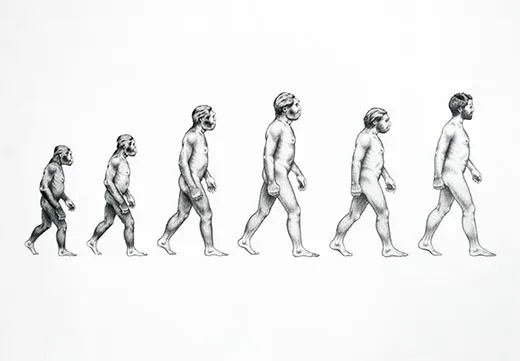
7. We’re all apes.
It’s kind of deflating, isn’t it? Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection can be inspiring: perhaps you’re awed by the vastness of geologic time or marvel at the variety of Earth’s creatures. The ability to appreciate and understand nature is just the sort of thing that is supposed to make us special, but instead it allowed us to realize that we’re merely a recent variation on the primate body plan. We may have a greater capacity for abstract thought than chimps do, but we’re weaker than gorillas, less agile in the treetops than orangutans and more ill-tempered than bonobos.
Charles Darwin started life as a creationist and only gradually came to realize the significance of the variation he observed in his travels aboard the Beagle. For the past 151 years, since On the Origin of Species was published, people have been arguing over evolution. Our ape ancestry conflicts with every culture’s creation myth and isn’t particularly intuitive, but everything we’ve learned since then—in biology, geology, genetics, paleontology, even chemistry and physics—supports his great insight.
8. Cultures throughout history and around the world have engaged in ritual human sacrifice.
Say you’re about to die and are packing some supplies for the afterlife. What to take? A couple of coins for the ferryman? Some flowers, maybe, or mementos of your loved ones? If you were an ancient Egyptian pharaoh, you’d have your servants slaughtered and buried adjacent to your tomb. Concubines were sacrificed in China to be eternal companions; certain Indian sects required human sacrifices. The Aztecs slaughtered tens of thousands of people to inaugurate the Great Pyramid of Tenochtitlan; after sacred Mayan ballgames, the losing team was sometimes sacrificed.
It’s hard to tell fact from fiction when it comes to this particularly gruesome custom. Ritual sacrifice is described in the Bible, Greek mythology and the Norse sagas, and the Romans accused many of the people they conquered of engaging in ritual sacrifice, but the evidence was thin. A recent accumulation of archaeological findings from around the world shows that it was surprisingly common for people to ritually kill—and sometimes eat—other people.
9. We’ve already changed the climate for the rest of this century.
The mechanics of climate change aren’t that complex: we burn fossil fuels; a byproduct of that burning is carbon dioxide; it enters the atmosphere and traps heat, warming the surface of the planet. The consequences are already apparent: glaciers are melting faster than ever, flowers are blooming earlier (just ask Henry David Thoreau), and plants and animals are moving to more extreme latitudes and altitudes to keep cool.
Even more disturbing is the fact that carbon dioxide lingers in the atmosphere for hundreds of years. We have just begun to see the effects of human-induced climate change, and the predictions for what’s to come range from dire to catastrophic.
10. The universe is made of stuff we can barely begin to imagine.
Everything you probably think of when you think of the universe—planets, stars, galaxies, black holes, dust—makes up just 4 percent of whatever is out there. The rest comes in two flavors of “dark,” or unknown stuff: dark matter, at 23 percent of the universe, and dark energy, at a whopping 73 percent:
Scientists have some ideas about what dark matter might be—exotic and still hypothetical particles—but they have hardly a clue about dark energy. … University of Chicago cosmologist Michael S. Turner ranks dark energy as “the most profound mystery in all of science.”
The effort to solve it has mobilized a generation of astronomers in a rethinking of physics and cosmology to rival and perhaps surpass the revolution Galileo inaugurated on an autumn evening in Padua. … [Dark energy] has inspired us to ask, as if for the first time: What is this cosmos we call home?
But astronomers do know that, thanks to these dark parts, the universe is expanding. And not only expanding, but expanding faster and faster. Ultimately, everything in the universe will drift farther and farther apart until the universe is uniformly cold and desolate. The world will end in a whimper.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/laura-helmuth-240.jpg)



/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/laura-helmuth-240.jpg)

