Biology
Rare 'Doomsday' Oarfish Surfaces in California, Just the 20th Discovered in the State Since 1901
Kayakers spotted and hauled ashore the 12-foot-long oarfish, a deep-sea species known for its connection to earthquakes in Japanese folklore
The World's Largest Animal Genome Belongs to an Odd, Air-Breathing Fish
Scientists sequenced the 91 billion base pairs in the South American lungfish’s genome, setting a record and revealing insights into vertebrate evolution
Rare Fossils Give Clues to How Tardigrades Survived Mass Extinctions by Hitting the Snooze Button
Scientists have only four known tardigrade fossils, which preserve insights into how the hardy critters evolved their hibernation-like superpower of cryptobiosis
These Mesmerizing Anemones Have a Glowing Layer of Protection
Marine biologists discovered that a protein that boosts fluorescent output also enables an antioxidant property
Your Microwave Is Teeming With Bacteria, Study Suggests
Researchers found thriving communities of microbes in microwave ovens used in home kitchens, shared spaces and laboratories
Rare 1-in-100-Million 'Cotton Candy' Lobster Found off the Coast of New Hampshire
A rare genetic mutation gives the crustacean its unique hues but also makes it more vulnerable to predators
Parasites Are Everywhere. Why Do So Few Researchers Study Them?
Aging parasitologists are working hard to inspire more students to enter the field
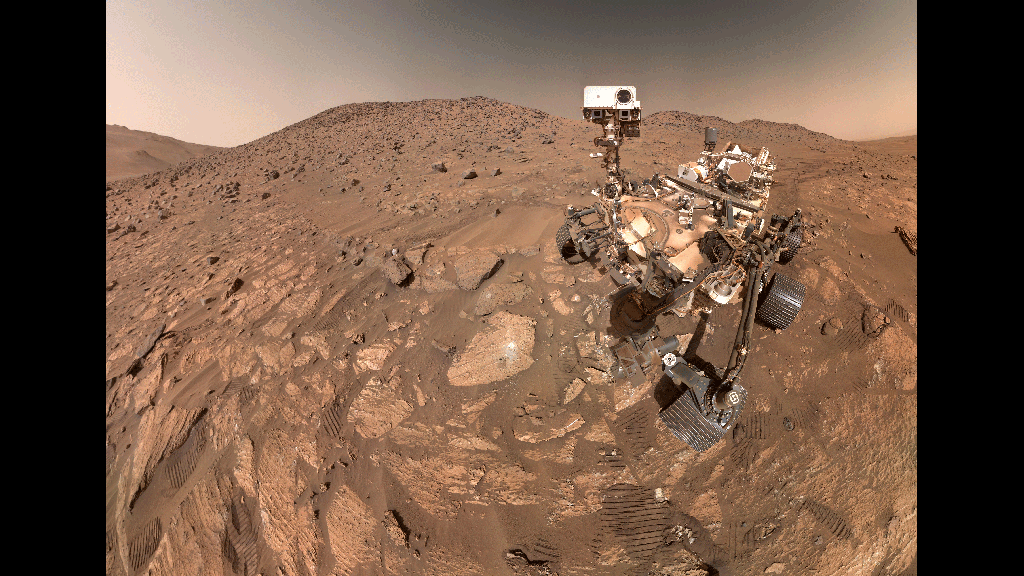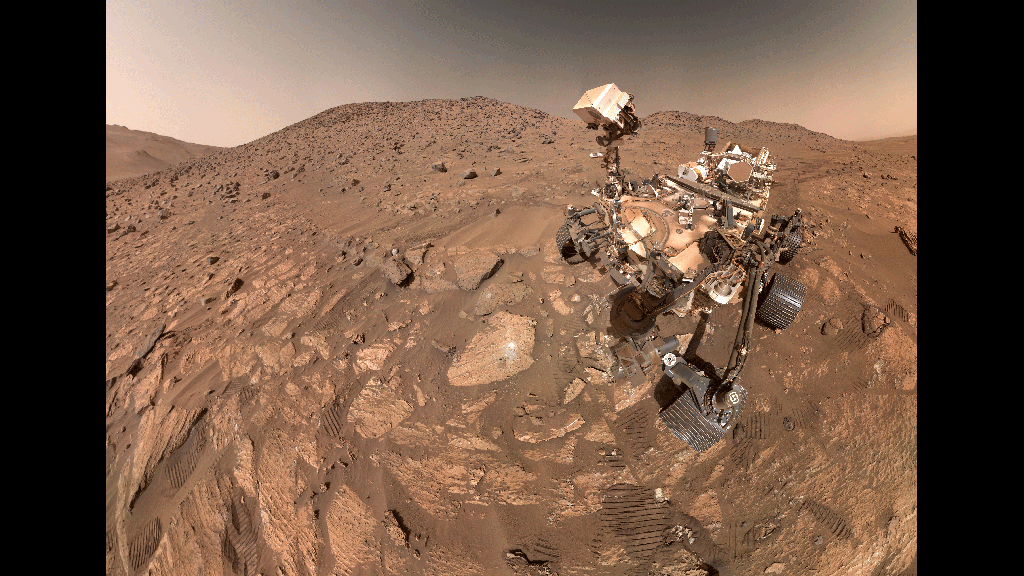
Mars Rover Finds Three Possible Signs of Ancient Life on a Single Rock
Scientists were cautiously optimistic about Perseverance's discovery, though they indicated further research is needed before drawing definitive conclusions
How to Sweat Like an Olympian
This summer, don’t be embarrassed by those pit stains or your drenched workout clothes. Our expert on the science of sweat says perspiration is what makes humans faster, higher and stronger
Look Into a 'Mega Den' of 2,000 Slithering Rattlesnakes With This Live Stream in Colorado
Run by researchers at Cal Poly, the stream is part of a citizen science initiative that aims to change the public's perception of the much-maligned reptiles
Watch Chatty Beluga Families Migrate With These Stunning Live Cams in Canada
Polar Bears International and Explore.org are once again capturing video footage and audio recordings of the social marine mammals as tens of thousands congregate in the Churchill River this summer
3D DNA Preserved for 52,000 Years in Freeze-Dried Woolly Mammoth Remains
For the first time, researchers have mapped ancient genetic material in unprecedented detail
The Wild Story of What Happened to Pablo Escobar’s Hungry, Hungry Hippos
Ever since the demise of the infamous drug kingpin, his pet hippos have flourished, wreaking havoc on the ecosystem and terrorizing local communities
Ancient DNA Unravels the Mysteries of the Dingo, Australia's Wild Dog
Researchers dove into thousands of years of evolutionary history, revealing new insights about the iconic, though sometimes vilified, canines
Carpenter Ants Perform Life-Saving Amputations to Treat Leg Injuries
A new study provides the first evidence of non-human animals performing amputations on others to improve their odds of survival
How Deep-Sea Comb Jellies Hold Their Shape Under Crushing Pressure
The delicate sea creatures fall apart when brought to the surface but can survive miles deep in the ocean due to special cell wall structures, according to a new study
Charlotte the 'Pregnant Virgin' Stingray Dies After Diagnosis of Reproductive Disease
The animal drew attention earlier this year for becoming pregnant despite having no male ray in her tank
Honeybees Can Sniff Out Lung Cancer, Scientists Suggest
New research opens the door for doctors to one day use bees as a living diagnostic tool
These Stunning Butterflies Flew 2,600 Miles Across the Atlantic Ocean Without Stopping
Researchers combined several lines of evidence to solve the mystery of why a group of painted ladies, which do not live in South America, were found fluttering on a beach in French Guiana
Meet the Forgotten Woman Who Revolutionized Microbiology With a Simple Kitchen Staple
Fanny Angelina Hesse introduced agar to the life sciences in 1881. A trove of unpublished family papers sheds new light on her many accomplishments
Page 3 of 87
:focal(1024x770:1025x771)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/59/63/59631b01-509a-4f2d-9094-b22eb8aa4d0b/455679878_888638413299980_5119357422845754426_n.jpg)
:focal(2000x1505:2001x1506)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/b8/63/b863fe13-8270-4ba6-8d7a-baff88e850ff/south_american_lungfish_lepidosiren_paradoxa_1.jpg)
:focal(1331x701:1332x702)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/84/ea/84eaccf4-aa95-4c71-83fa-e165dc095671/screenshot_2024-08-19_at_23348_pm.png)
:focal(800x602:801x603)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/e2/d5/e2d5021b-4081-4824-a682-eaa650a7175e/smithsonian-wide-34_web.jpg)
:focal(640x427:641x428)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/e7/f2/e7f24549-f508-4363-aab0-6eb2aa8a96c7/kitchen-7706307_1280.jpg)
:focal(2016x1517:2017x1518)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/ef/f9/eff9a27e-4247-4e6b-ad69-a97262c94224/cotton_candy_lobster-seacoast_science_center-july_2024_-_3.jpeg)
:focal(800x602:801x603)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/58/ed/58ed036d-8bc4-4be2-ae67-d07a0c2e33a6/img_9264_web.jpg)
:focal(700x527:701x528)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/f7/ef/f7ef0851-8e9c-4456-b3dc-505faae37ff3/smithmag-podcast-s02-ep12-sweat-article.jpg)
:focal(600x400:601x401)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/1f/87/1f8744da-9a25-4eff-aa47-8bc6b5d45b10/41bb6a1f-9f09-352e-7ab5-f1d358e05407.jpg)
:focal(600x400:601x401)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/e1/61/e161ee8e-6cc6-4049-9842-b8072931a225/kieran-mciver-1311209.jpg)
:focal(600x400:601x401)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/9d/03/9d03e8f0-5b0e-4445-b90a-69b96ccf49b0/imrs_1.png)
:focal(700x527:701x528)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/3d/c2/3dc23c07-7efb-4254-830f-45cab1968fb5/smithmag-podcast-s02-ep11-hippo-article.jpg)
:focal(1067x701:1068x702)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/f4/d0/f4d0fb37-4f26-455a-a8c4-ada959fa2a8a/gettyimages-80254810.jpg)
:focal(350x297:351x298)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/24/49/24499a13-136e-448c-b662-f611f6d0f795/low-res_video_still_image__woundcare_and_amputation_in_c_maculatus_credit_danny_buffat.jpg)
:focal(1060x713:1061x714)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/78/11/7811e0eb-8364-458a-a9b4-14a582663169/gettyimages-90050101.jpg)
:focal(1024x770:1025x771)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/29/a1/29a10843-cb53-4808-b49a-fd229a727237/430063553_706533311658853_4996824608781781526_n.jpg)
:focal(1024x683:1025x684)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/94/10/9410cbf2-768e-4115-8542-924193a2ee66/2048px-honey_bee_apis_mellifera.jpeg)
:focal(2117x1250:2118x1251)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/b0/c3/b0c341da-9979-4fef-8ae7-1865608d7fe4/una_mariposa_cardera_a_punto_de_emprender_el_vuelo_autor_roger_vila.jpg)
:focal(700x527:701x528)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/eb/e4/ebe4e883-241d-40cc-b92b-3a96ce2fb152/hesse.jpg)